Getting to 5G: Comparing 4G and 5G System Requirements
September 7, 2017
5G isn't just an incremental improvement over 4G — it's the next major evolution of mobile communication technology with performance improvements of several orders of magnitude over today's networks. 5G does not replace 4G, it simply enables a huge diversity of tasks that 4G cannot perform. 4G will continue to advance in parallel with 5G, as the network to support more routine tasks. 5G will enable services yet to be imagined, in a world where national economies are driven by sophisticated communications networks.
Let's explore what 5G technology is, compare some of the characteristics of 4G and 5G, and look at the path to 5G deployment.
What 5G Technology Is

- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) requiring hundreds of megahertz (MHz) of channel bandwidth using new frequencies for mobile wireless — from 2.5 gigahertz (GHz) for 4G LTE Pro and 3.5GHz for 5G, to tens of gigahertz and beyond into the millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum
- Ultra efficient for streaming data, taking full advantage of carrier aggregation (CA) and massive multiple input/multiple output (MIMO)
- Fixed wireless, giving more choices to get 20 gigabit per second (Gbps) connections to your home and business
- Wireless infrastructure, using beam steering and high-power gallium nitride (GaN), ideally suited to adaptive-array steerable antennas
- Low latency for real-time connections enabling autonomous vehicles and augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR)
- Internet of Things (IoT) connecting more than a trillion devices to the Internet in the next ten years with extremely low data rates, battery life greater than ten years, and the longest possible communication range
Comparing 4G and 5G
The figure below provides a comparison of the performance characteristics and technical specifications of 4G and 5G technology.
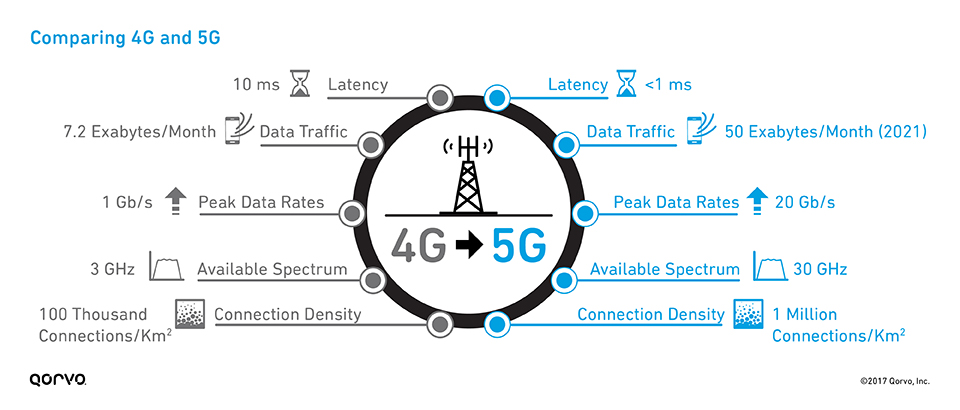
The following table summarizes the major differences between 4G and 5G technology.
| 4G (Today, Before Further Developments) | 5G | |
|---|---|---|
|
Latency |
10 ms |
Less than 1 ms |
|
Peak data rates |
1 Gbps |
20 Gbps |
|
Number of mobile connections |
8 billion (2016) |
11 billion (2021) |
|
Channel bandwidth |
20MHz 200kHz (for Cat-NB1 IoT) |
100MHz below 6GHz 400MHz above 6GHz |
|
Frequency band |
600MHz to 5.925 GHz |
600MHz–mmWave (for example, 28GHz, 39GHz, and onward to 80 GHz |
|
Uplink waveform |
Single-carrier frequency division multiple access (SC-FDMA) |
Option for cyclic prefix orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (CP-OFDM) |
|
User Equipment (UE) transmitted power |
+23 decibel-milliwatts (dBm) except 2.5GHz time- division duplexing (TDD) Band 41 where +26dBm, HPUE is allowed IoT has a lower power-class option at +20dBm |
+26dBm for less than 6GHz 5G bands at and above 2.5GHz |
Currently, use cases are being defined, new radio access technologies are being developed, and carrier field trials are being conducted. The Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) standards body is harmonizing and globalizing these new ideas into a unified specification.
By adopting LTE Advanced (LTE-A), carriers are making considerable progress toward the speed goals for 5G (see figure), but more work is required.

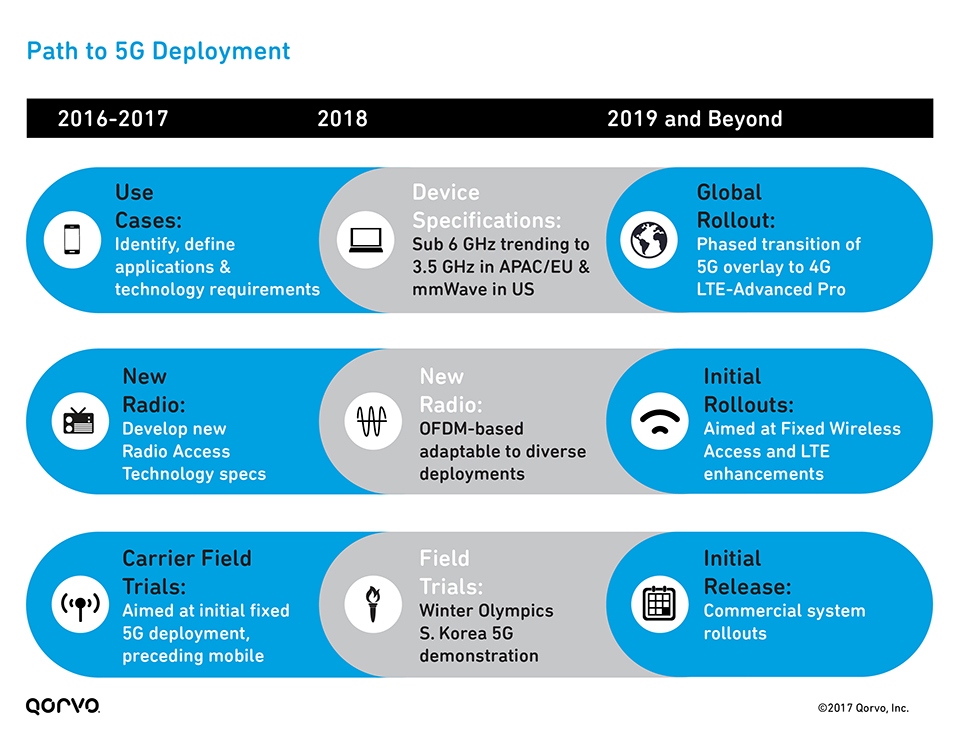
The Path to 5G Deployment
Enhancing the mobile wireless experience is a step-by-step pathway for carriers, requiring further expansion and development of 4G and moving toward LTE-A technologies. Carriers are currently in the midst of developing software-defined networks (SDNs), heterogeneous networks (HetNets), and low power networks. Finally, in 2019 and beyond, global 5G rollouts and initial commercial releases will begin (see figure).
– Excerpted with permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc., from 5G RF For Dummies.
Want more details about what's to come with 5G? Download a copy of our latest e-book, 5G RF For Dummies® Second Edition. Interested in learning how the next generation of Wi-Fi will fit in with the deployment of 5G and expansion of the IoT? Read more in our white paper: 5G or Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)?
Have another topic that you would like Qorvo experts to cover? Email your suggestions to the Qorvo Blog team and it could be featured in an upcoming post. Please include your contact information in the body of the email.
